Cervical spine exercises are a cornerstone in physical therapy‚ aiding in pain relief‚ improved posture‚ and enhanced muscle strength. These exercises‚ often combined with manual therapy and ergonomic tips‚ provide a comprehensive approach to addressing neck discomfort and promoting long-term spinal health.
Importance of Cervical Spine Exercises
Cervical spine exercises play a vital role in maintaining neck health and preventing injuries. They improve mobility‚ reduce stiffness‚ and strengthen muscles‚ enhancing overall spinal stability. Regular exercises can alleviate chronic pain‚ address poor posture‚ and restore functional movement. These exercises are essential for rehabilitation after injuries or surgeries‚ promoting faster recovery and reducing the risk of long-term damage. Strengthening the cervical region also improves nerve function‚ reducing symptoms like numbness or tingling. Consistent practice enhances daily activities and reduces the likelihood of recurring neck pain‚ making cervical exercises a cornerstone of physical therapy for both treatment and prevention of cervical spine-related conditions.
Understanding the Anatomy of the Cervical Spine
The cervical spine consists of seven vertebrae‚ muscles‚ ligaments‚ and nerves that enable flexible neck movement and support the skull. Its complex structure ensures stability and protects vital neural pathways.
Key Structures: Vertebrae‚ Muscles‚ Ligaments‚ and Nerves
The cervical spine comprises seven vertebrae (C1-C7)‚ which provide structural support and protect the spinal cord. Muscles‚ including flexors‚ extensors‚ and rotators‚ enable movement and stability. Ligaments connect vertebrae‚ ensuring joint stability‚ while nerves‚ such as the cervical plexus and brachial plexus‚ regulate sensory and motor functions. These components work together to facilitate neck mobility‚ maintain posture‚ and protect neural pathways essential for bodily functions. Understanding these structures is crucial for designing effective physical therapy exercises targeting the cervical spine;
Benefits of Cervical Spine Exercises
Cervical spine exercises enhance mobility‚ reduce pain‚ and strengthen neck muscles. They improve posture‚ alleviate stiffness‚ and promote long-term spinal health‚ preventing future discomfort and injuries.
Improving Range of Motion and Reducing Pain
Cervical spine exercises play a crucial role in improving range of motion and reducing pain. Gentle stretches and mobilization techniques enhance flexibility‚ allowing for smoother neck movements. Isometric exercises‚ such as neck flexion and extension‚ strengthen muscles without putting excessive strain on the spine. These exercises also help alleviate stiffness and discomfort‚ particularly in individuals with chronic neck pain. Manual therapy techniques‚ including massage and joint mobilization‚ further complement these exercises by reducing muscle tension and improving joint mobility. Consistent practice of these exercises can significantly enhance quality of life by restoring functional movement and minimizing pain‚ promoting overall cervical spine health.
Strengthening Neck Muscles and Enhancing Posture
Strengthening neck muscles through targeted exercises is essential for maintaining proper posture and spinal alignment. Exercises like neck retractions and chin tucks help build endurance and stability in the cervical region. Scapular stabilization exercises further enhance posture by addressing shoulder and upper back muscle imbalances. Strengthening these muscles reduces the risk of forward head posture‚ a common issue in individuals with neck pain. Improved posture not only alleviates strain on the cervical spine but also promotes better breathing and overall physical comfort. Regular practice of these exercises‚ combined with manual therapy techniques‚ can lead to long-term improvements in both muscle strength and postural alignment.
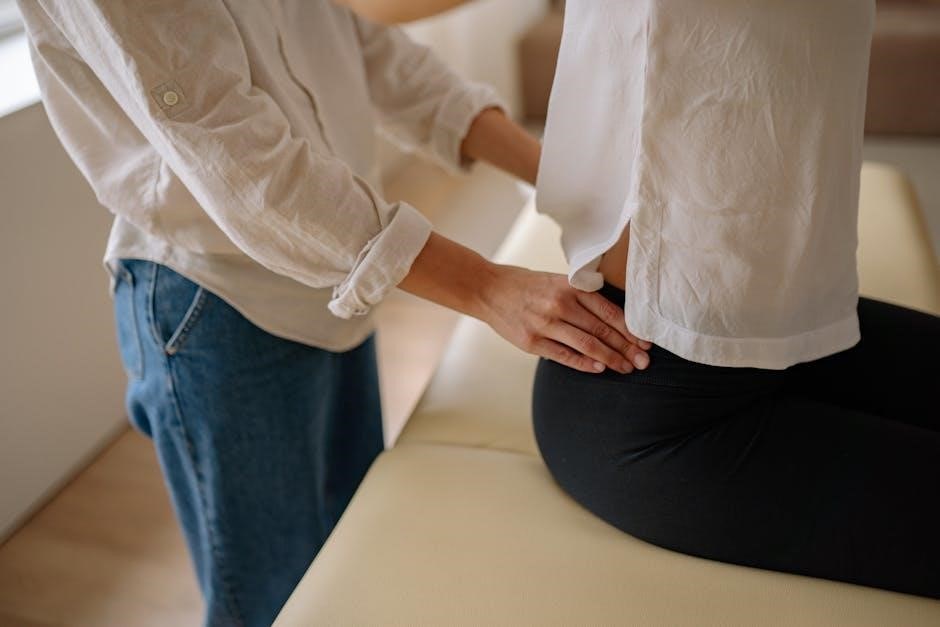

Common Cervical Spine Exercises in Physical Therapy
Cervical spine exercises include isometric neck exercises‚ retractions‚ and scapular stabilization. These therapies‚ often combined with manual or self-manual techniques‚ improve flexibility‚ strength‚ and posture‚ addressing neck discomfort effectively.
Isometric Neck Exercises: Flexion‚ Extension‚ and Side Bends
Isometric neck exercises‚ such as flexion‚ extension‚ and side bends‚ involve contracting muscles without moving the head. These exercises strengthen cervical muscles and improve posture. Flexion requires gently pressing the forehead against resistance‚ while extension involves pressing the back of the head. Side bends involve tilting the head toward the shoulder. Each exercise is held for 5-10 seconds and repeated 8-12 times. They are low-impact‚ reducing strain on joints‚ and are particularly beneficial for those with neck pain or limited mobility. Regular practice can enhance muscle endurance‚ stabilize the cervical spine‚ and alleviate discomfort‚ making them a cornerstone in physical therapy routines.
Neck Retraction and Chin Tucks
Neck retraction and chin tucks are fundamental exercises targeting the cervical spine. To perform a chin tuck‚ stand or sit upright‚ look straight ahead‚ and gently tuck the chin toward the chest‚ holding for 15-30 seconds. Neck retraction involves pulling the head back‚ keeping the jaw level‚ and holding for 5-10 seconds. These exercises strengthen the deep cervical flexors‚ improve posture‚ and reduce neck pain. They are often recommended for individuals with forward head posture or chronic neck discomfort. Regular practice enhances spinal alignment‚ reduces muscle strain‚ and promotes long-term neck stability‚ making them a key component of physical therapy routines for cervical health.
Scapular Stabilization Exercises
Scapular stabilization exercises are essential for improving cervical spine health by enhancing shoulder blade movement and muscle activation. These exercises‚ such as shoulder blade squeezes and wall slides‚ strengthen the muscles around the scapula‚ reducing neck strain. By improving scapular stability‚ individuals can reduce the burden on the cervical spine‚ alleviating pain and enhancing posture. Regular practice of these exercises promotes proper shoulder mechanics and reduces the risk of chronic neck discomfort. They are often performed in conjunction with cervical exercises to ensure comprehensive spinal stability and long-term pain relief‚ making them a vital component of physical therapy routines for neck health.
When to Start Cervical Spine Exercises
Cervical spine exercises should begin after consulting a healthcare provider‚ typically post-injury or surgery‚ once acute pain subsides‚ to safely promote mobility and prevent stiffness.
Post-Injury or Post-Surgery Rehabilitation Guidelines
Post-injury or post-surgery rehabilitation for the cervical spine typically follows a phased approach. Phase I focuses on reducing pain and inflammation‚ often using immobilization and gentle isometric exercises. Phase II introduces controlled mobility and strengthening exercises‚ such as chin tucks and gentle range-of-motion movements‚ to restore function without aggravating the injury. Phase III involves progressive resistance and dynamic exercises to enhance strength and stability. It’s crucial to avoid heavy lifting or repetitive strain during recovery. A supervised physical therapy program ensures safe progression and prevents re-injury. Adherence to these guidelines helps optimize recovery and restore normal cervical function.
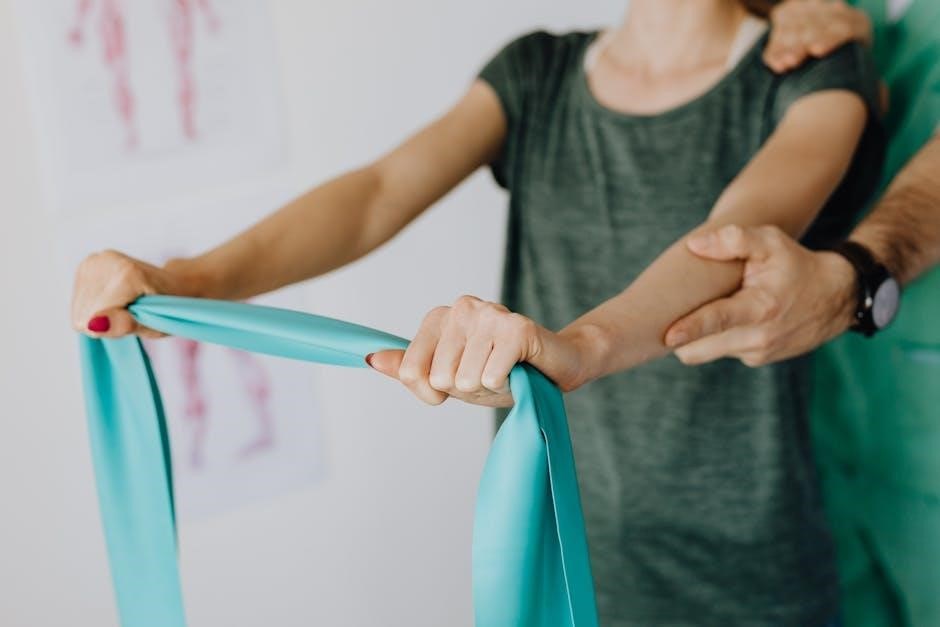

Manual Therapy Techniques for the Cervical Spine
Manual therapy‚ including massage and joint mobilization‚ is essential for cervical spine treatment. These techniques relieve muscle tension‚ improve mobility‚ and are tailored to individual patient needs.
Massage‚ Joint Mobilization‚ and Soft Tissue Techniques
Massage‚ joint mobilization‚ and soft tissue techniques are integral to cervical spine therapy. Massage reduces muscle tension and improves blood flow‚ while joint mobilization enhances spinal mobility. Soft tissue techniques‚ such as myofascial release‚ target tight connective tissue to restore flexibility. These methods are often combined with exercises to address pain‚ stiffness‚ and limited range of motion. They are particularly effective for chronic neck pain and postural imbalances. Manual therapy‚ including these techniques‚ is tailored to individual needs‚ promoting relaxation and functional improvement. Regular application of these techniques‚ alongside therapeutic exercises‚ supports long-term cervical spine health and reduces the risk of recurring discomfort.

Preventing Neck Pain Through Exercise
Regular cervical exercises‚ postural awareness‚ and ergonomic adjustments help prevent neck pain. Strengthening muscles and improving flexibility reduce strain‚ promoting long-term spinal health and discomfort avoidance.
Postural Awareness and Ergonomic Tips
Postural awareness and ergonomic adjustments are crucial for preventing neck pain. Maintaining a neutral spine alignment during daily activities reduces strain on cervical structures. Ensure proper workspace setup: monitor at eye level‚ keyboard close‚ and chair height adjusted to support a 90-degree elbow bend. Avoid prolonged static postures and take regular breaks to stretch. Strengthening core and shoulder muscles also enhances posture. Incorporate ergonomic tips like using a supportive pillow and avoiding heavy bags. Consistency in these practices minimizes the risk of developing neck pain‚ promoting long-term spinal health and comfort.