The 54 basic surgical instruments are essential tools in surgical procedures‚ ensuring efficiency‚ precision‚ and positive patient outcomes. These instruments cover various stages of surgery‚ from cutting to suturing‚ and are indispensable for surgeons.
Importance of Surgical Instruments in Medical Procedures
Surgical instruments are vital tools that facilitate various medical procedures‚ ensuring precision‚ efficiency‚ and positive patient outcomes. They are essential for diagnosing and treating conditions‚ alleviating pain‚ and saving lives. These instruments enable surgeons to perform tasks ranging from cutting and dissecting tissues to suturing and stapling‚ making them indispensable in every surgical setting. Their proper use enhances surgical efficiency‚ reduces complications‚ and improves recovery times. The 54 basic surgical instruments are fundamental in equipping healthcare professionals with the means to deliver high-quality care‚ emphasizing their critical role in modern medicine and patient well-being.
Overview of the 54 Basic Surgical Instruments

The 54 basic surgical instruments represent a comprehensive collection of tools essential for modern surgical practices. These instruments are categorized into functional groups‚ including cutting‚ dissecting‚ clamping‚ grasping‚ suturing‚ retracting‚ and suctioning. Each tool is designed for specific tasks‚ ensuring precision and efficiency during procedures. This standardized set is vital for surgeons and surgical technologists‚ as it provides the necessary resources to perform a wide range of operations effectively. Understanding these instruments is fundamental for mastering surgical techniques and delivering high-quality patient care across various medical specialties.
Classification of Surgical Instruments
Surgical instruments are categorized by function‚ including cutting/dissecting‚ clamping/occluding‚ grasping/holding‚ suturing/stapling‚ retracting/exposing‚ suctioning‚ and viewing. This classification ensures efficient organization and use during procedures.
Cutting and Dissecting Instruments
Cutting and dissecting instruments are essential for precise tissue separation and incisions. These tools include scalpels‚ surgical scissors‚ knives‚ and rongeurs. Scalpels are used for initial incisions‚ while scissors cut tissues with curved or straight blades. Surgical knives provide sharp‚ precise cuts‚ and rongeurs handle tougher materials like bone. These instruments are versatile‚ ensuring accurate dissection and tissue preparation. Their design varies to suit specific surgical needs‚ making them indispensable in all procedures. Proper use of these tools enhances surgical efficiency and patient outcomes‚ highlighting their critical role in modern surgery.
Clamping and Occluding Instruments
Clamping and occluding instruments are vital for controlling bleeding and maintaining surgical site access. These tools include clamps like Kelly and mosquito clamps‚ which temporarily occlude blood vessels. They are designed to grip without causing tissue damage‚ ensuring precise control during procedures. Occluding instruments also help in managing fluid flow‚ preventing complications. Their robust construction and ergonomic design make them reliable for surgeons‚ enhancing surgical efficiency and safety. These instruments are crucial for minimizing blood loss and maintaining a clear operating field‚ making them indispensable in various surgical specialties.
Grasping and Holding Instruments
Grasping and holding instruments are designed to securely grip tissues or objects during surgery‚ minimizing tissue trauma. Common examples include Allis forceps‚ Babcock forceps‚ and DeBakey forceps. These tools feature ratcheted or non-ratcheted handles‚ allowing precise control. They are used for retracting‚ lifting‚ or holding tissues in place‚ ensuring clear access to the surgical site. Their ergonomic design enhances comfort and dexterity‚ making them indispensable for surgeons. These instruments play a critical role in maintaining tissue integrity and facilitating smooth surgical procedures across various specialties.
Suturing and Stapling Instruments
Suturing and stapling instruments are vital for closing wounds and joining tissues during surgery. These include needle holders‚ surgical staplers‚ and suture scissors. Needle holders feature sturdy jaws to grip and manipulate needles‚ while staplers ensure rapid and precise tissue alignment; Suture scissors are used to cut sutures neatly. These tools are designed for both manual and mechanical suturing‚ offering versatility in various surgical contexts. They ensure secure tissue approximation‚ promoting healing and minimizing post-operative complications. Their precision and durability make them essential for achieving optimal surgical outcomes across diverse procedures and specialties.
Retracting and Exposing Instruments
Retracting and exposing instruments are used to retract soft tissues and organs‚ providing optimal visibility and access to the surgical site. Common types include retractors like Gelpi and Weitlaner‚ which are designed to hold tissues in place during procedures. These instruments are essential for minimizing tissue trauma while maximizing exposure. They come in various shapes and sizes to suit different surgical needs‚ ensuring precise control and reducing operative complications. Retractors play a critical role in enhancing surgical precision and efficiency‚ making them indispensable in modern surgical practices across various specialties and procedures.
Suctioning Instruments
Suctioning instruments are vital for removing fluids‚ blood‚ and debris from the surgical site‚ ensuring clear visibility and a clean operating field. These tools‚ such as suction tips and tubing‚ are designed to maintain a sterile environment and prevent complications. They are categorized based on their suction strength and application‚ with specific types used for delicate tissue areas or heavy fluid extraction. Proper use of suctioning instruments enhances surgical precision‚ reduces operative time‚ and improves patient safety by minimizing the risk of infection and promoting unobstructed access to the surgical area throughout the procedure.
Viewing Instruments
Viewing instruments are crucial for providing optimal visualization during surgical procedures. Tools like surgical loupes‚ headlights‚ and endoscopes enable surgeons to magnify and illuminate specific areas‚ enhancing precision. These devices are often integrated with cameras for real-time monitoring‚ benefiting both surgical teams and patients. Their use minimizes blind spots‚ reduces operative complications‚ and ensures accurate tissue dissection. By improving visibility‚ viewing instruments play a key role in modern surgery‚ contributing to better outcomes and safer practices across various specialties. They are essential for maintaining clarity and control in complex surgical environments‚ making them indispensable in the operating room.

Common Names of Surgical Instruments

Surgical instruments include widely recognized tools such as scalpels‚ forceps‚ retractors‚ surgical scissors‚ and knives. These names are fundamental to understanding basic surgical instrumentation and their functions.
Surgical Scissors
Surgical scissors are versatile cutting tools used in various procedures. They feature opposing blades‚ which may be curved or straight‚ designed for precise tissue cutting and dissection. Available in different types‚ such as Mayo and Metzenbaum scissors‚ they cater to specific surgical needs‚ ensuring efficiency and accuracy. These instruments are essential in every operating room‚ aiding surgeons in delicate tasks with their sharp‚ durable edges. Proper care and sterilization are crucial to maintain their effectiveness and longevity‚ making them a cornerstone in surgical instrumentation.
Surgical Knives
Surgical knives are fundamental tools used to make precise incisions in tissues. Designed with sharp‚ high-carbon stainless steel blades‚ they ensure clean cuts and minimal tissue damage. Available in various shapes and sizes‚ such as scalpel blades‚ they are tailored for specific procedures. Handles are typically ergonomic‚ providing comfort and control for surgeons during operations. Proper maintenance‚ including regular sharpening‚ is essential to uphold their cutting efficiency. As a primary instrument in every surgical setup‚ surgical knives play a critical role in the success of medical procedures‚ enabling accurate and effective tissue dissection.
Scalpels
Scalpels are essential tools in surgical procedures‚ primarily used for making precise incisions. They consist of a handle and a detachable blade‚ typically made from high-carbon stainless steel for sharpness and durability. Scalpels are available in various sizes and shapes‚ catering to different surgical needs‚ from delicate skin incisions to deeper tissue cuts. Their ergonomic design ensures a firm grip‚ reducing fatigue during long operations. Proper sterilization and maintenance are crucial to prevent infection and maintain their effectiveness. As one of the most frequently used instruments‚ scalpels are indispensable in every surgical setting‚ enabling surgeons to perform procedures with accuracy and confidence.
Forceps
Forceps are vital surgical instruments designed for grasping‚ holding‚ and manipulating tissues or objects during procedures. Available in various types‚ such as Allis‚ Babcock‚ and DeBakey forceps‚ they cater to specific surgical needs. Their sturdy construction ensures a secure grip‚ minimizing tissue damage. Forceps are indispensable in surgeries‚ enabling precise tissue handling and reducing operative trauma. As a core component of the 54 basic surgical instruments‚ they play a critical role in enhancing surgical accuracy and efficiency‚ making them an essential tool for surgeons across all specialties.
Retractors
Retractors are essential surgical instruments used to expose and maintain access to the operative site by gently holding back tissues or organs. Available in various types‚ such as Deaver‚ Richardson‚ and Gelpi retractors‚ they are tailored for specific surgical needs. Retractors are crucial for providing a clear surgical field‚ enhancing visibility‚ and reducing operative complexity. Constructed from durable materials like stainless steel‚ they ensure reliability and sterility. As part of the 54 basic surgical instruments‚ retractors play a vital role in facilitating precise dissection and minimizing tissue trauma‚ making them indispensable in modern surgical practices across all specialties.
Historical Development and Manufacturing of Surgical Instruments
Surgical instruments have evolved from ancient stone tools to precision-engineered devices‚ with Sialkot emerging as a global hub for manufacturing. Their production combines traditional craftsmanship with modern technology.
Key Manufacturers and Their Contributions
Prominent manufacturers like Sialkot-based companies have revolutionized surgical instrument production‚ supplying over two-thirds of the world’s basic tools. These manufacturers blend traditional craftsmanship with modern technology‚ ensuring precision and durability. Their contributions include producing high-quality instruments such as scalpels‚ forceps‚ and retractors‚ which are essential for global surgical practices. Many companies specialize in specific instruments‚ driving innovation in materials and design. Their adherence to international standards has made them reliable suppliers to medical industries worldwide‚ enabling advancements in surgical care and patient outcomes.
Global Impact of Surgical Instrument Manufacturing
Surgical instrument manufacturing has a profound global impact‚ enabling advancements in healthcare and surgical care. Countries like Pakistan‚ particularly Sialkot‚ are renowned for producing high-quality instruments‚ contributing significantly to the global medical industry. These tools are used in diverse surgical specialties worldwide‚ ensuring precise and efficient procedures. The manufacturing of basic surgical instruments supports millions of surgeries annually‚ improving patient outcomes and saving lives. Additionally‚ this industry drives economic growth‚ creates jobs‚ and fosters innovation‚ making it a cornerstone of modern healthcare systems. Reliable production ensures global access to essential instruments‚ advancing surgical practices worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the 54 basic surgical instruments? Essential tools for surgeries‚ covering cutting‚ dissecting‚ suturing‚ and more.
- Why are these instruments important? They ensure precision‚ efficiency‚ and safety in medical procedures.
- How are they classified? Categorized by function: cutting‚ clamping‚ grasping‚ suturing‚ retracting‚ suctioning‚ and viewing.
- Who manufactures them? Key manufacturers include companies in Sialkot‚ Pakistan‚ and global suppliers.
- Are they used across all specialties? Yes‚ they are fundamental tools in various surgical disciplines.
Uses of Basic Surgical Instruments in Different Specialties
Basic surgical instruments are versatile tools used across various medical specialties. In general surgery‚ scalpels and scissors are essential for incisions and tissue dissection. Orthopedic surgeries rely on bone cutters and retractors for precise bone adjustments. Ophthalmology uses fine forceps and suction tools for delicate eye procedures. Cardiovascular surgeries employ clamps and suturing instruments to repair or replace heart structures. Neurosurgery utilizes specialized retractors and dissecting instruments for brain and spinal cord operations. Plastic surgery often involves scalpels‚ scissors‚ and suturing tools for grafting and reconstruction. Each specialty adapts these instruments to meet specific procedural needs‚ ensuring optimal outcomes.
Proper Care and Maintenance of Surgical Instruments
Proper care and maintenance of surgical instruments are crucial for ensuring their longevity and effectiveness. Immediate cleaning after use prevents tissue residue buildup. Sterilization methods like autoclaving or chemical disinfection are essential to eliminate pathogens. Instruments should be stored in dry‚ protective cases to avoid damage. Regular lubrication of movable parts prevents rust and ensures smooth operation. Routine maintenance checks help identify wear and tear early‚ preventing malfunctions during procedures. Proper handling and storage practices are vital for maintaining the quality and functionality of these critical tools‚ ensuring they remain reliable for future surgical procedures.
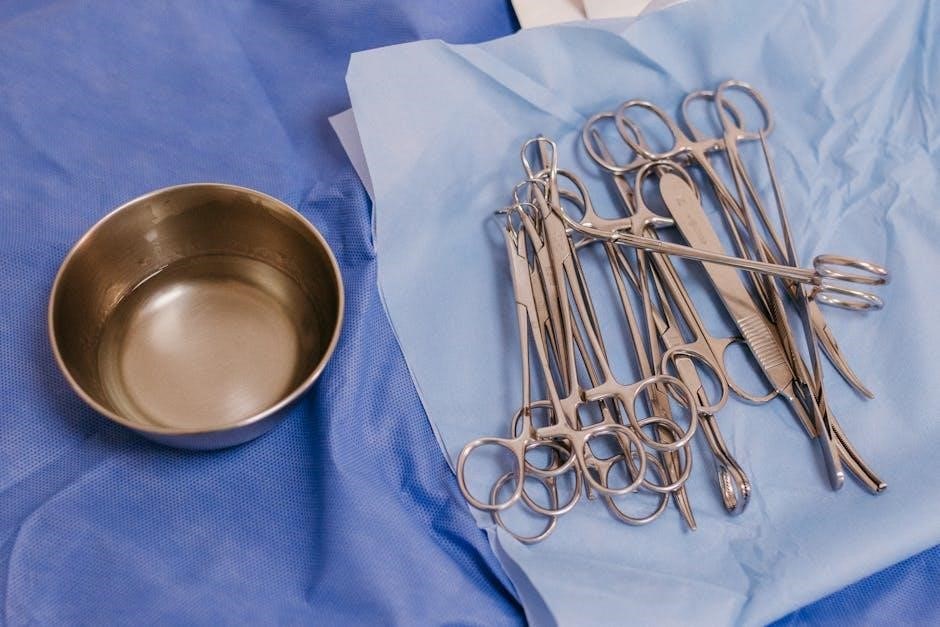
Key Takeaways
The 54 basic surgical instruments form the cornerstone of modern surgical practices‚ enabling precise and efficient procedures. Understanding their classifications‚ functions‚ and proper maintenance is essential for surgeons and surgical technologists. These instruments‚ ranging from scalpels to retractors‚ are categorized into cutting‚ clamping‚ grasping‚ suturing‚ and retracting tools. Proper care‚ including sterilization and storage‚ ensures their longevity and effectiveness. Mastery of these tools is vital for optimizing surgical outcomes and patient safety. Their global manufacturing and widespread use highlight their critical role in advancing medical care and saving lives. Grasping their fundamentals is indispensable for every surgical professional.